- Published on
Athoni: Web Optimization - Achieving Sub-100ms Load Times for Subsequent Visits
- Authors

- Name
- Jack Nguyen
Table of Contents
I. Demo
Website: https://www.athoni.com

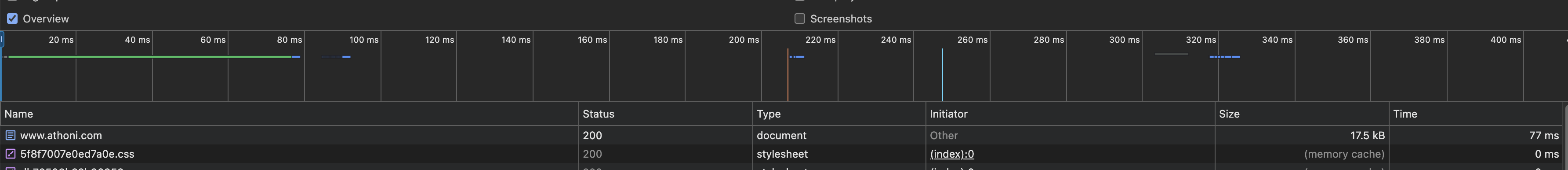


II. Performance
1. Cloudflare CDN - Next.js
CDN for All Website Bundles
To ensure faster load times, I configured Cloudflare CDN in our Next.js project to deliver all website bundles. Here’s the configuration:
next.config.js
const nextTranslate = require('next-translate-plugin')
const nextConfig = {
assetPrefix:
process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production' && process.env.NEXT_PUBLIC_CDN_URL
? process.env.NEXT_PUBLIC_CDN_URL
: '',
}
module.exports = nextTranslate(nextConfig)
After setting up the CDN, I updated our environment variables to include the CDN URL:
.env
NEXT_PUBLIC_CDN_URL=https://cdn.athoni.com
This is the result of our implementation:
ex: https://athoni.com/_next/static/chunks/pages/_app-1a2b3c4d.js -> https://cdn.athoni.com/_next/static/chunks/pages/_app-1a2b3c4d.js
When debuging in "Network" tab, you will see the resources are loaded from the CDN URL with "cf-cache-status: HIT" with "Cloudflare" as the server.
CDN for All Resources (S3)
I also optimized the delivery of resources like images and videos by configuring Cloudflare to handle our S3 public URLs efficiently.
Add the following to your Cloudflare DNS settings:
| CNAME | Name | Domain |
|---|---|---|
| CNAME | cdn | your S3 public URL |
Then, update your S3 bucket policy to allow Cloudflare to access your resources:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"AWS": "arn:aws:iam::cloudflare:role/cloudflare"
},
"Action": "s3:GetObject",
"Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::your-bucket-name/*"
}
]
}
2. Next.js <Image> Component
The Next.js <Image> component automatically optimizes images for better quality and faster load times. This reduces the strain on our website and provides a better user experience.
Read here: Next.js Image Component
3. Using WebP for Images
By converting images to the WebP format, I achieved smaller file sizes without compromising quality, improving load speeds significantly.
4. Prefetch Link
Prefetching DNS and preconnecting to our CDN ensures quicker loading by preparing resources in advance:
<link rel="dns-prefetch" href="//cdn.athoni.com" />
<link rel="preconnect" href="https://cdn.athoni.com/" crossorigin="true" />
Read here: DNS Prefetch, Preconnect
III. SEO
1. Server-Side Rendering - Next.js
Server-side rendering ensures that search engines can access pre-rendered pages, improving SEO and making our content easily discoverable.
Read here: Next.js Server-Side Rendering
2. Meta Social Links
Meta tags enhance how our pages appear when shared on social media, ensuring that previews look professional and engaging.
Example:
<meta property="og:title" content="Athoni" />
<meta property="og:description" content="Athoni - Find your dream job in IT" />
<meta property="og:image" content="https://cdn.athoni.com/static/img/og-image.png" />
<meta property="og:url" content="https://www.athoni.com" />
<meta name="twitter:card" content="summary_large_image" />
<meta name="twitter:title" content="Athoni" />
<meta name="twitter:description" content="Athoni - Find your dream job in IT" />
<meta name="twitter:image" content="https://cdn.athoni.com/static/img/og-image.png" />
3. Localization
Our site supports multiple languages, currently English and Vietnamese, to cater to a diverse audience and improve user experience globally.
Read here: Next.js Internationalized Routing
Example for SEO:
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="en" href="https://www.athoni.com/" />
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="vi" href="https://www.athoni.com/vi" />
4. Sitemap.xml
I created a dynamic sitemap to guide search engines effectively. Here’s our implementation:
import { Component } from 'react'
const createURL = (path, multiLang = true) => {
return `<url>
<loc>${process.env.NEXT_PUBLIC_ORIGIN_URL}${path}</loc>
<changefreq>monthly</changefreq>
${
multiLang &&
['en', 'vi']
.map(
(lang) =>
`<xhtml:link
rel='alternate'
hreflang='${lang}'
href="${process.env.NEXT_PUBLIC_ORIGIN_URL}${
lang === 'en' ? '' : '/' + lang
}${path}"></xhtml:link>`
)
.join('')
}
</url>`
}
const createSitemap = () => `<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<urlset xmlns="http://www.sitemaps.org/schemas/sitemap/0.9" xmlns:xhtml="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
${createURL('')}
${createURL('/privacy-policy')}
${createURL('/terms-conditions')}
</urlset>`
class Sitemap extends Component {
static async getInitialProps({ res }) {
try {
res.setHeader('Content-Type', 'text/xml')
res.write(createSitemap())
res.end()
} catch (error) {
res.write('Not Found!')
res.end()
}
}
}
export default Sitemap
5. Robots.txt
Our robots.txt file directs search engines efficiently. Here’s what it looks like:
User-agent: *
Allow: /
Sitemap: https://www.athoni.com/sitemap.xml
With these optimizations, our landing page is now faster, more responsive, and SEO-friendly. If you’re looking to improve your own website’s performance and visibility, these steps are a great place to start.